Comprehensive List of Anti-Inflammatory Drugs for Arthritis Relief
Managing arthritis pain and inflammation effectively often requires the use of anti-inflammatory drugs. These medications play a crucial role in reducing swelling, stiffness, and discomfort caused by arthritis. In this article, we provide a comprehensive list of anti-inflammatory drugs and their uses for arthritis relief, helping patients and caregivers make informed decisions.
1. Understanding Anti-Inflammatory Drugs for Arthritis
Anti-inflammatory drugs fall into several categories, each serving a specific purpose in treating arthritis symptoms. Common types include:
- Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): Reduce pain and inflammation.
- Corticosteroids: Powerful drugs for severe inflammation.
- Biologics: Target specific parts of the immune system.
- DMARDs (Disease-Modifying Anti-Rheumatic Drugs): Slow disease progression.
2. Table of Common Anti-Inflammatory Drugs
Here’s a detailed table listing common anti-inflammatory drugs used for arthritis relief, their categories, and uses:
| Drug Name | Category | Usage | Potential Side Effects |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ibuprofen (Advil) | NSAID | Mild to moderate pain relief | Stomach upset, ulcers |
| Naproxen (Aleve) | NSAID | Long-lasting inflammation control | Dizziness, heartburn |
| Celecoxib (Celebrex) | NSAID (COX-2 Inhibitor) | Severe arthritis pain | Increased risk of heart issues |
| Prednisone | Corticosteroid | Short-term severe inflammation | Weight gain, high blood sugar |
| Methotrexate | DMARD | Slows rheumatoid arthritis | Nausea, liver damage |
| Etanercept (Enbrel) | Biologic | Blocks inflammation-causing proteins | Risk of infection, injection site reactions |
| Adalimumab (Humira) | Biologic | Treats rheumatoid arthritis symptoms | Headaches, increased infection risk |
3. Choosing the Right Anti-Inflammatory Drug
Selecting the right medication depends on several factors, including:
- Type of Arthritis: Osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and psoriatic arthritis require different approaches.
- Severity of Symptoms: Mild symptoms may require over-the-counter NSAIDs, while severe cases may need DMARDs or biologics.
- Side Effect Profile: Patients should consider potential side effects and consult with their doctor.
- Other Medical Conditions: People with certain conditions (e.g., heart disease) may need alternative treatments.
4. Lifestyle Tips to Complement Medication
While anti-inflammatory drugs are effective, combining them with lifestyle changes can further improve arthritis symptoms:
| Tip | Details |
|---|---|
| Balanced Diet | Eat anti-inflammatory foods like fish, nuts, and leafy greens. |
| Regular Exercise | Engage in low-impact activities like swimming or walking. |
| Weight Management | Maintaining a healthy weight reduces pressure on joints. |
| Heat and Cold Therapy | Alternate between heat packs and cold compresses for pain relief. |
5. Consult Your Doctor Before Starting Medication
While this comprehensive list of anti-inflammatory drugs serves as a guide, always consult a healthcare provider before starting any new medication. A doctor will evaluate your specific condition, symptoms, and medical history to recommend the most effective treatment plan.
Explore
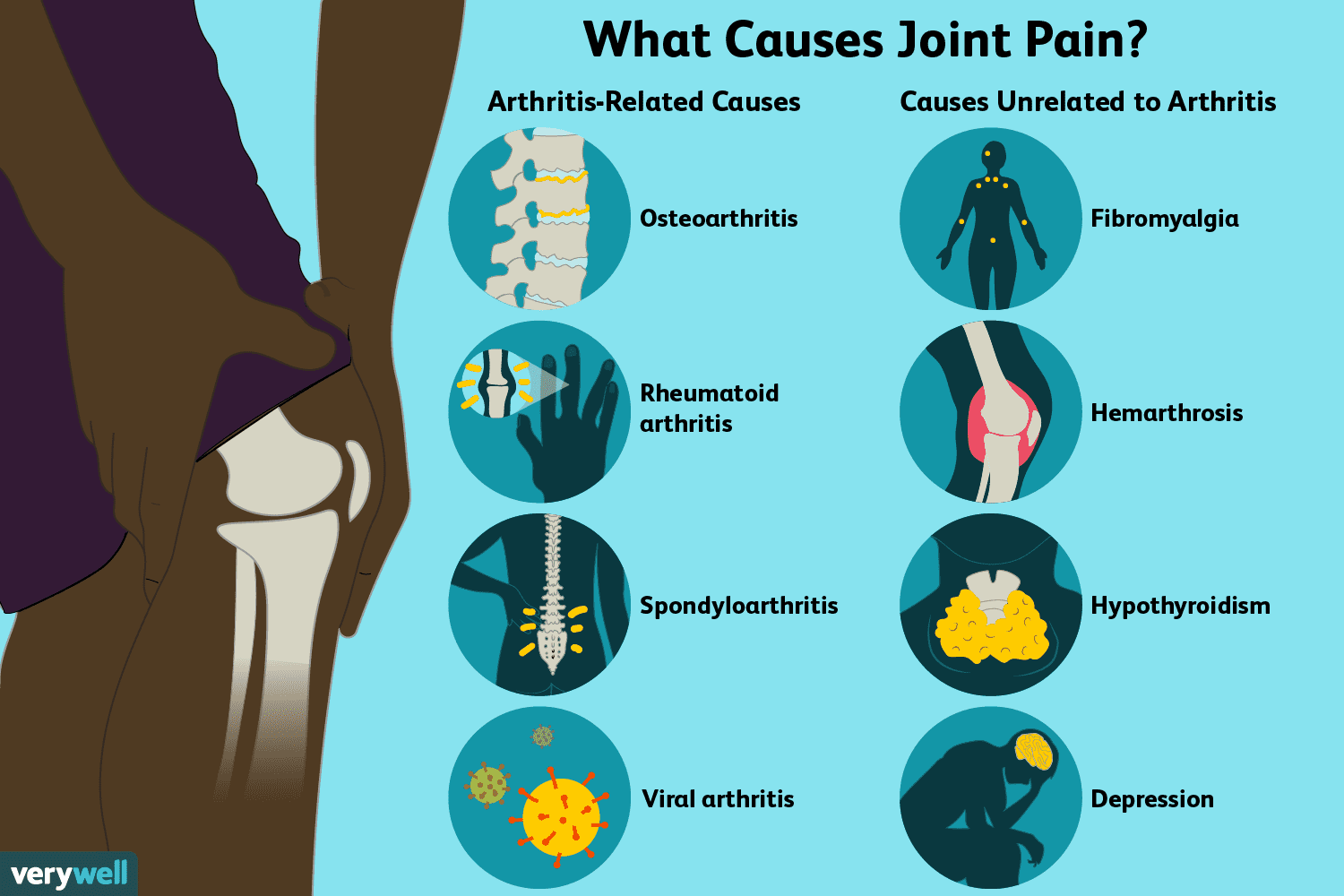
Most Effective and Newest Medications for Arthritis Pain Relief

How to Achieve Fast Bowel Relief: Tips and Treatments for Quick Relief

List of Medicare Advantage Plans 2024 & 2025

2025 List of Top 15 PCB Manufacturers in the USA for Your Project

Find Financial Freedom: Best Debt Relief Companies in the USA

Finding the Best Weight Loss Clinics Near You: A Comprehensive Guide

Where Can I Buy Cheap and Good Quality Solar Panels? A Comprehensive Guide
Purchase Structured Settlements: A Comprehensive Guide
