OT Cyber Security: Protecting Critical Infrastructure from Cyber Threats
As the world becomes increasingly interconnected, the security of OT (Operational Technology) systems has become a top priority for industries like manufacturing, energy, transportation, and utilities. OT cyber security refers to the protection of industrial control systems (ICS), SCADA systems, and other technology used to monitor and control critical infrastructure. Unlike traditional IT systems, OT environments often operate with legacy equipment and protocols, making them particularly vulnerable to cyber threats. This article will explore the importance of OT cyber security, common vulnerabilities, and best practices for securing operational technology.
Why OT Cyber Security is Crucial
OT systems control vital processes in sectors such as energy generation, water treatment, manufacturing, and transportation. As these systems become more connected to the internet and corporate IT networks, they face greater risks of cyber attacks. In recent years, incidents like the Stuxnet attack on Iranian nuclear facilities have highlighted the devastating impact that cyber threats can have on critical infrastructure.
Without robust OT cyber security measures, organizations risk:
- Operational Disruptions: Cyber attacks can cause system outages or equipment malfunctions, leading to production downtime.
- Financial Loss: A successful cyber attack can result in expensive recovery efforts, loss of revenue, and penalties for non-compliance.
- Reputation Damage: A breach in OT systems can damage an organization’s reputation, especially if it affects public services or critical infrastructure.
- Safety Hazards: Cyber attacks on OT systems can compromise safety protocols, posing risks to employees and the public.
Common OT Cyber Security Vulnerabilities
OT systems have unique vulnerabilities that differ from traditional IT networks. Here are some of the most common security risks in OT environments:
| Vulnerability | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Legacy Systems | Many OT systems use outdated hardware and software with known vulnerabilities. | Increased risk of exploitation due to unpatched systems. |
| Lack of Network Segmentation | OT systems often share the same network with IT systems, creating a potential attack vector. | A breach in the IT network can lead to access to critical OT systems. |
| Unprotected Remote Access | Remote access solutions are often poorly secured, allowing cybercriminals to exploit vulnerabilities. | Unauthorized access and control over OT systems. |
| Insufficient Security Awareness | Many employees are not trained in cyber security best practices specific to OT environments. | Human error leading to security breaches or data leaks. |
| Inadequate Patch Management | Failure to regularly update OT systems with the latest security patches. | Exploitation of known vulnerabilities by cybercriminals. |
Best Practices for OT Cyber Security
To safeguard operational technology, companies must implement a multi-layered approach to cyber security. Here are some of the best practices to follow:
1. Network Segmentation
Ensure that OT systems are isolated from corporate IT networks to prevent a cyber attack from spreading across systems. Segmentation reduces the risk of lateral movement from IT to OT.
2. Regular Security Audits
Conduct regular security assessments and vulnerability scans to identify weaknesses in your OT systems. This proactive approach helps prevent attacks before they occur.
3. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Implement MFA for remote access to OT systems. This adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide two or more forms of identification.
4. Employee Training
Regularly train employees on OT cyber security protocols and best practices. Ensuring that staff are aware of the risks can help prevent human error from leading to security breaches.
5. Patch Management
Ensure that OT systems are kept up to date with the latest security patches. Vulnerabilities in outdated systems are prime targets for cybercriminals.
6. Incident Response Plan
Develop and regularly update an incident response plan to ensure your team is prepared to respond quickly and effectively in the event of a cyber attack.
Key OT Cyber Security Solutions
When it comes to protecting OT environments, there are several specialized solutions designed to strengthen security:
| Solution | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Industrial Firewalls | Firewalls designed specifically to protect OT networks from unauthorized access. | Enhanced network segmentation and intrusion detection. |
| Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) | Systems that monitor OT networks for suspicious activity and potential breaches. | Quick identification of abnormal behavior, minimizing risk. |
| Endpoint Protection | Security solutions that protect devices like sensors, controllers, and remote terminals. | Prevents malware from infecting critical OT devices. |
| Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) | Solutions that aggregate and analyze security data from across the OT environment. | Provides real-time monitoring and advanced threat detection. |
| Vulnerability Management Tools | Tools that help identify, assess, and remediate vulnerabilities in OT systems. | Reduces the attack surface by addressing security weaknesses. |
Conclusion: Strengthening OT Cyber Security for the Future
As OT systems continue to evolve and become more interconnected, the need for OT cyber security will only grow. Cyber attacks targeting operational technology can have far-reaching consequences, including financial loss, operational disruption, and safety hazards. By following best practices like network segmentation, regular security audits, and employee training, businesses can mitigate these risks and protect their critical infrastructure.
With the right combination of security tools, solutions, and proactive measures, organizations can ensure their OT environments are resilient against the ever-evolving landscape of cyber threats. It’s essential to stay ahead of emerging risks by continuously adapting security strategies to safeguard operational technology now and in the future.
Explore
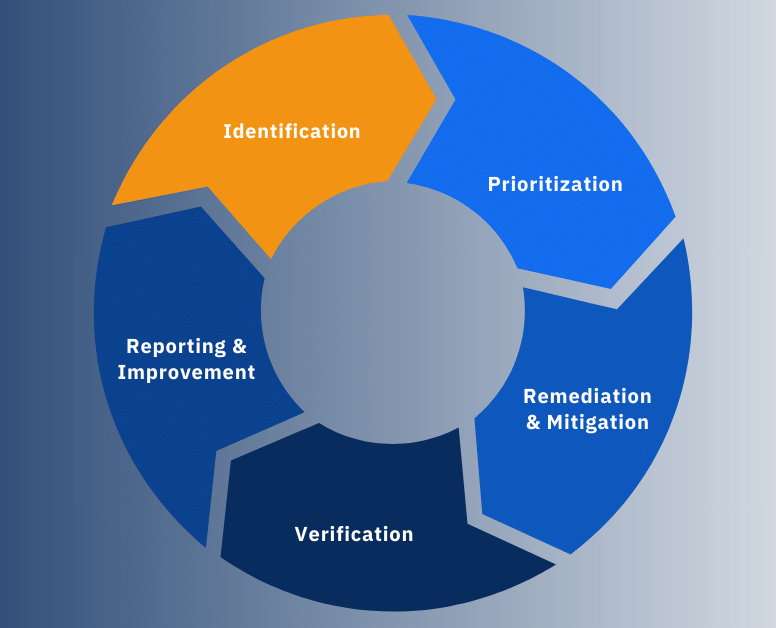
Vulnerability Management in Cyber Security: Protecting Your Systems from Threats
Network Security Management: Protecting Your Network from Cyber Threats

Managed Security Services: Protecting Your Business from Cyber Threats

Sewage Damage Cleanup Services: The Key to Protecting Your Home from Health Hazards

Cloud Hosting Showdown: Comparing the Best Providers for Speed, Security, and Scalability

Enterprise Password Manager: Enhance Security and Simplify Password Management

Best Cybercrime Degree Online 2025: Unlock Your Future in Digital Security

Best Home Improvement Contractors Near Me
